Have you ever thought about how a customer journey resembles the infinity symbol ♾️?
It has no defined beginning or clear end; rather, it moves in a continuous loop of awareness, consideration, experience, loyalty, and then starts again. Every interaction, no matter how small, reshapes the relationship between the customer and your brand, leaving an impact that determines the continuity of this journey.
This is where the importance of the Customer Journey Map (CJM) comes in. It is not merely a tool to analyze user behavior, but a language through which you can understand your customers’ emotions and translate their needs into exceptional human experiences. It enables you to see beyond the numbers and helps you grasp the true story your customer experiences with you at every stage, from the very first discovery to loyalty and advocacy, and then onto a new journey in an endless circle.
Definition of the Customer Journey Map
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the path a customer takes with your brand, from the first interaction to the loyalty stage. This journey illustrates the customer’s steps, needs, and emotions during their engagement with you, helping you understand and enhance their experience at every stage.
Benefits of Creating a Customer Journey Map
The customer journey acts as a compass guiding your understanding of your customers’ experience. It provides a comprehensive view of their path with your brand and helps you align your strategy toward being customer-centric. Some of the main benefits include:
• Gaining a deeper understanding of the customer’s needs, emotions, and expectations at every stage of their journey.
• Improving touchpoints and reducing challenges by identifying pain points and addressing them to ensure a smooth and pleasant experience.
• Increasing satisfaction and customer retention by enhancing post-purchase experiences and support.
• Enhancing the customer experience by improving interaction quality and ensuring ongoing satisfaction.
• Achieving harmony across company departments such as marketing, sales, support, and development to deliver a unified and consistent experience.
• Boosting sales and revenue by building long-term relationships with happy customers who are more likely to repurchase.
• Increasing loyalty and encouraging brand advocacy by exceeding customer expectations and building lasting trust.
• Optimizing resource allocation and costs based on real data and genuine insights rather than assumptions.
7 Core Components of the Customer Journey Map
These components form the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of the customer experience and for analyzing every step a customer takes while interacting with your brand, from the first moment of awareness to loyalty and advocacy. Below are the main components that a successful customer journey map is built upon:
1. Journey Stages
To simplify the customer experience and enhance every interaction, the journey is divided into major stages that reflect the customer’s steps, needs, and behaviors, revealing opportunities for improvement, increased satisfaction, and loyalty.
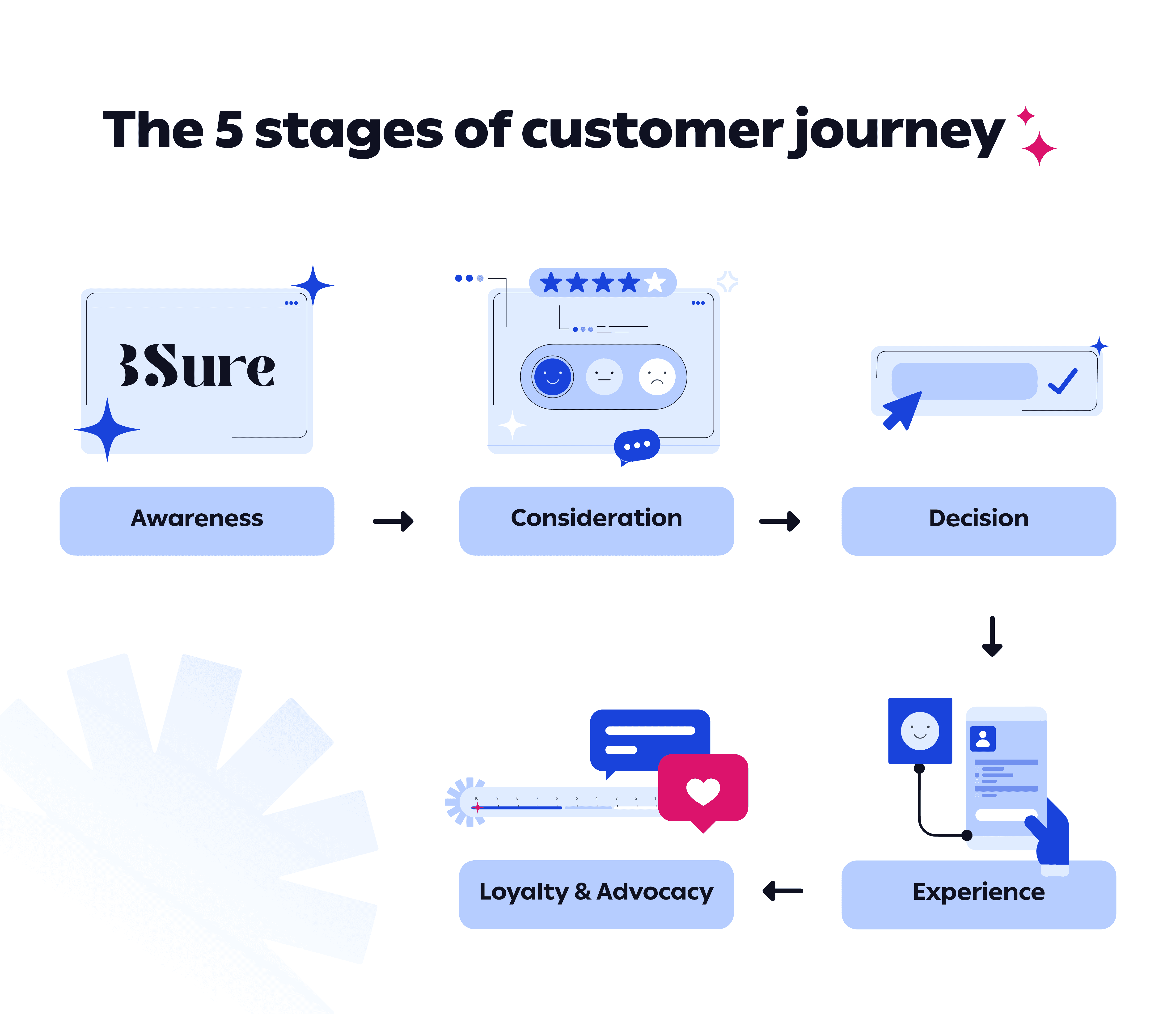
The table below illustrates 5 key customer stages, along with a description, objective, and practical examples to help understand their real-world application:
Stage | Description | Objective | Practical Example |
Awareness | The customer discovers your brand for the first time, through an ad, content, or recommendation. | Introducing the customer to your brand and creating a first impression. | A social media ad introducing the new product. |
Consideration | The customer compares your options with competitors, looking at features, pricing, and ratings. | Building trust and helping the customer make an informed decision. | Reading customer reviews on the website or watching a product demo video. |
Decision / Purchase | The customer decides to buy and completes the process. | Facilitating purchase and making the experience smooth and seamless. | A simple and fast checkout page with multiple payment options and free shipping. |
Post-Purchase / Experience | The customer experiences the product or service post-purchase and evaluates satisfaction levels. | Ensuring customer satisfaction and resolving any issues during usage. | Communicating with the customer to confirm product receipt and provide technical support if needed. |
Loyalty & Advocacy | A satisfied customer returns to purchase again or recommends the brand to others. | Strengthening loyalty and building a sustainable base of customer advocates. | A loyalty program offering discounts on future purchases or encouraging customers to leave positive reviews. |
2. Touchpoints
Every moment the customer interacts with the brand, whether via website, advertisement, physical store, or customer service.
3. Customer Actions
Illustrates what the customer does at each stage: researching, comparing, contacting, purchasing, using the product, etc.
4. Emotions
How the customer feels at each stage: excitement, confusion, frustration, satisfaction, etc.
5. Pain Points
Obstacles or problems the customer encounters that negatively affect their experience.
6. Opportunities
Areas for improvement that can be leveraged to enhance the experience and increase customer satisfaction.
7. Metrics
Performance indicators used to assess the effectiveness of the experience, such as conversion rates, satisfaction, and loyalty.
9 Practical Steps to Create a Customer Journey Map
1. Define Scope & Objective
• Identify the question or problem you want the journey map to answer, e.g., why do customers abandon their carts, or how can we encourage repeat purchases?
• Choose a specific scope, a journey for a particular product, with a specific customer segment, in a defined context. If the journey is too broad, focus may be lost.
• Ensure all project participants share a common understanding of the objective and scope.
Depending on the goal of the customer journey map, the structure and strategies you use may vary. Some possible objectives include:
Objective | Description |
Improve customer retention and experience | Make every interaction smooth and satisfying while addressing pain points to enhance loyalty. |
Increase conversion rates | Improve customer steps at critical stages to increase the percentage of customers completing a purchase. |
Improve products | Develop products and services aligned with actual customer needs and feedback. |
Enhance customer communication | Build effective and seamless communication channels throughout the journey to make the customer feel supported and cared for. |
Boost loyalty and advocacy | Turn happy customers into brand advocates through repeat purchases and product recommendations. |
2. Research & Insights
Data is the foundation for genuinely understanding the customer experience:
• Customer Interviews: Conduct interviews with customers to understand their motivations, obstacles they faced, and what they feel at each stage of their journey.
• Digital Surveys: Use digital surveys to collect quantitative feedback on specific experiences, such as customer satisfaction with a particular service or product.
• Digital Data Analysis: Track customer behavior on your website or app, including conversion rates, time on page, error rates, and drop-off points.
• Team Feedback & Social Listening: Leverage insights from support and sales teams, and review comments on social media and other digital platforms.
The purpose of this step is to build an accurate picture of the customer experience as they see it, rather than relying on hypothetical assumptions.
3. Data Analysis and Segmentation
After collecting the data, review and analyze it to identify trends and key points. Then segment customers into groups based on demographic characteristics and behaviors, to better understand each segment and determine the appropriate improvements for each group.
4. Building Customer Personas
Create customer profiles based on the data you collected, including challenges, motivations, communication preferences, and goals for each group. Then validate the accuracy of these personas by comparing them with internal data or updating them through focus groups to ensure they realistically represent your customers.
Define representative customer personas or segments:
• Fake name, background, needs, goals, behaviors, obstacles.
Example:
“Sami, 28 years old, uses food delivery apps, prefers paying via electronic card, and values fast delivery and high-quality packaging. Obstacles: finds it difficult to track orders, sometimes experiences delays in delivery or payment issues.”
Using these personas, you can precisely focus on every touchpoint: what the customer thinks, what they feel, and what they need.
5. Identifying Customer Touchpoints
The best way to identify touchpoints is to view them from the customer’s perspective, imagine each step they take in every stage previously mentioned. Key touchpoints throughout the customer journey include:
Before the transaction:
• Ads and digital marketing campaigns
• Online testimonials and reviews
• Your social media activity
• Product reviews on e-commerce platforms
• Word-of-mouth recommendations
During the transaction:
• Physical store, website, or catalog
• Interaction with sales or support staff
• Call center or customer service
After the transaction:
• Invoices, inquiries, and return services
• Product support and post-purchase service
• Customer feedback surveys, product newsletters, and thank-you cards
After identifying touchpoints, ask yourself whether there are any obstacles the customer may face during the journey, or if there are missing touchpoints that need more support.
6. Map the Current Journey
Now, use a visual diagram (paper-based or digital using tools like Canva, UXPressia, or others) to map the journey stages, including:
• Customer actions at each stage
• What they are thinking
• What they are feeling
• Channels / media used
• Pain points and difficulties
• Potential opportunities for improvement
You can also add an Emotional Journey Line to show how the customer’s emotions fluctuate between satisfaction and frustration throughout the journey stages.
7. Pain Points & Opportunities
After completing the journey map:
• Identify stages and touchpoints where the customer may feel frustrated or hesitant.
• Determine the possible causes of these difficulties, such as a hard-to-use website, limited payment options, or delayed shipping.
• Extract opportunities to improve the experience, such as simplifying processes, providing additional support, or delighting the customer unexpectedly.
8. Future-State Journey
Based on the previous analysis, design the ideal customer journey by:
• Removing complex or unnecessary steps
• Adding support points and interactive communication with the customer
• Enhancing alignment across all channels used
• Increasing personalization and intelligence, such as offering suggestions based on customer behavior
• Ensuring smooth transitions between stages without any gaps that could affect the customer experience
9. Monitoring & Continuous Improvement
• Implement changes step by step
• Track performance using metrics such as customer satisfaction, wait times, and conversion rates
• Ask customers for feedback after changes
• Adjust the map according to results and changes in the market or customer behavior
• Regularly review the map with your team and decision-makers to continuously improve the experience
VoC + CJM = Complete Understanding of the Customer Experience
Customer Journey Maps (CJM) and Voice of the Customer (VoC) work together to provide a comprehensive understanding of the customer experience. VoC provides real data on customer opinions, while CJM organizes this data visually across interaction stages, helping companies identify pain points, enhance the experience, and increase loyalty.
Integrating VoC data makes maps more realistic and dynamic by including direct inputs like surveys, ratings, feedback, and social media comments, offering an accurate view of customer experiences and emotions at every stage.
VoC Integration Methodology in Journey Maps:
• Data Collection: From surveys, customer feedback, ratings, and social media comments
• Data Analysis: To identify patterns, emotions, pain points, and moments of satisfaction
• Data Mapping: Place the insights at each stage of the customer journey
• Continuous Improvement: Update the maps continuously to reflect the current customer experience accurately
This way, the Customer Journey Map becomes an effective tool to understand customers and continuously improve their experience based on real data.
How to Know if Your Map is Successful
You know your map is effective when you see its impact on the customer experience and business results clearly. Key indicators of success include:
1. Achieving Targeted Results: Such as increasing stage-to-stage conversion (from browsing to purchase) or reducing cart abandonment
2. Accurately Representing Customer Experience: The map truly reflects customer feelings and experiences, evident in higher satisfaction levels
3. Improving the Customer Journey: Reducing the time customers spend completing processes and increasing the percentage of returning or recommending customers
4. Readability and Applicability: Any team within the company can understand and act upon the map easily
5. Regular Updates and Flexibility: Reviewed and updated regularly using VoC data to ensure accuracy
6. Enhancing Revenue and Business Performance: Increasing sales, improving customer loyalty, and reducing complaints
In short, if you notice improvements in both customer satisfaction and business outcomes, your map is heading in the right direction.
8 Best Practices for Creating an Effective Customer Journey Map
Designing a customer journey map may seem complex at first, especially in large organizations or fast-growing companies. However, following a set of systematic practices makes the process clearer and more effective.
1. Collect Feedback from All Touchpoints
A successful journey map starts with genuinely listening to your customers. Ensure you gather feedback after every interaction, whether through support, sales, or digital platforms.
This step can easily be automated by sending short satisfaction surveys after each experience. The more data you collect, the more accurate your view of the customer journey, and the deeper your ability to enhance the experience.
2. Put Customer Needs First
The success of the journey map doesn’t rely solely on product quality, but on the smoothness of the experience the customer goes through. Remove obstacles and friction points that may hinder satisfaction, as even small improvements in the journey increase trust and loyalty to your brand.
3. Follow a Practical and Gradual Approach
Start small; focus first on a specific customer segment or a single core journey, then gradually expand the analysis to include other segments.
4. Test the Experience Yourself
Put yourself in the customer’s shoes, or ask a new user to go through the entire experience from start to finish. This step uncovers weaknesses that may not appear in reports or tables.
5. Use Storytelling
Turn the map into an interactive story describing the customer’s emotions at each stage, from first contact to loyalty. Storytelling humanizes the data and helps different teams understand the experience from the customer’s perspective.
6. Be Transparent and Set Clear Expectations
Clarify to your customers what they can expect from your service and what cannot be achieved at the moment. Transparency builds trust and reduces frustration caused by the gap between promises and reality.
7. Involve Customers in Development
Engage them in every update to the service or product. Continuously ask for feedback after any change; their opinions are the compass guiding your next improvements.
8. Consider the Map a Living Document
A customer journey map is not a one-time file; it is a living document that evolves continuously. Review it regularly and adjust it based on changing customer behaviors and market trends.
Conclusion:
Without this map, the customer experience remains random, as if you are walking a long, branching road without a guide, you don’t know where to start, where to go, or what awaits at the next turn.
Start today by mapping your customer journeys to see the full path and identify the points that delight customers and those that need improvement. With this perspective, every interaction becomes an opportunity to build a stronger and more sustainable relationship with your customers.
Create your survey or listen carefully to your customers’ voice with BSure, and start turning every experience into a step toward success.










